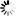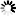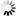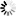Periodontal disease (also known as gum disease) is a serious health concern in cats and dogs. According to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), by the time they are 3 years old, many pets are already at risk for or suffering from gum disease.
The Consequences of Periodontal Disease in Cats & Dogs
Why Dental Care Matters!
Sponsored content from Jax & Cali
Periodontal disease (also known as gum disease) is a serious health concern in cats and dogs. According to the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), by the time they are 3 years old, many pets are already at risk for or suffering from gum disease.
When periodontal disease begins, there are usually no outward signs or symptoms. However, once it advances, gum disease can devastate your cats’ and dogs’ mouth, causing chronic pain, eroded gums, missing teeth, and bone loss - a fate hardly fair to our beloved best friends!
What Causes Periodontal Disease in Cats & Dogs?
When your cat or dog eats, bacteria from food particles and saliva begin forming a sticky film over the teeth called plaque. lf allowed to remain on the tooth's surface, plaque thickens, becomes mineralized and creates tartar (calculus). This tartar accumulates above and below the gum line leading to inflammation or infection called Gingivitis. Gingivitis which is seen as a reddening of the gums directly bordering the teeth is the early stage of periodontal disease.
The Impact of Periodontal Disease
This inflammation or infection of the tissues surrounding the tooth causes gum recession around the tooth's attachment – also known as periodontal tissue. By then, your pet may be living with chronic pain.
Some symptoms of severe gum disease include:
- Bleeding or red inflamed gums
- Loss of appetite or dropping food from the moth while eating
- Loose teeth
- Blood in the water bowl or on chew toys
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- "Talking" or making noises when a dog eats or yawns
- Bumps or lumps in the mouth
- Sneezing or nasal discharge (advanced gum disease in the upper teeth can destroy the bone between the nasal and oral cavity)
When left untreated, the infection often spreads deeper into the tooth socket, destroying the bone which can lead to tooth extraction which is not only uncomfortable for your pet but comes with a hefty veterinary bill. According to a recent article from Daily Paws, the average combined cost of tooth extraction, including x-rays, exams, and other hospitalization costs can range from $400 to over $1,000 per tooth.
Bacteria surrounding the roots gain can also access to the blood stream (“bacteremia”). Studies from the AVMA have shown that dogs with severe periodontal disease have more severe microscopic damage in their kidneys, heart muscle and liver than do dogs with less severe periodontal disease.
How to Prevent Periodontal Disease and Tooth Loss in Your Pet
So how can you protect your pet’s dental health?
- Brush your pet’s teeth regularly.
- For pets who are brushing-adverse, consider a dental product like Jax & Cali Toothbrush Wipes to easily reduce and inhibit bacterial growth.
- Dental foods and treats are specially formulated to help promote healthy teeth and gums in cats and dogs.
- Regular dental cleanings are important! Make sure to schedule an annual dental cleaning for your pet.
Have more than one pet or a pet on a prescription diet? Consider serving up your pet’s food in a SureFeed® Microchip Pet Feeder. Each bowl is opened by your pet’s unique microchip or RFID collar tag. Prevent food stealing between pets and accurately track when and how much food your pets are eating.
Brought to you by:
![<?php echo $store[store_name]; ?> flag](https://media.surepetcare.com/website/images/homepage_tiles/shopping-cart.png)